CRM in services has emerged as a game-changer, empowering businesses to elevate their customer interactions and drive operational efficiency. As we delve into this topic, we’ll explore the significance of CRM in the service industry, its key features, best practices, and future trends that are shaping the landscape.
CRM (Customer Relationship Management) serves as the backbone of modern service organizations, providing a comprehensive platform to manage customer data, streamline service processes, and enhance customer engagement. By leveraging CRM’s capabilities, businesses can gain a holistic view of their customers, tailor personalized experiences, and drive growth.
Introduction to CRM in Services
Customer relationship management (CRM) is a vital tool for businesses in the service industry. CRM systems help businesses manage customer interactions, track customer data, and provide personalized service. By implementing a CRM system, service businesses can improve customer satisfaction, increase sales, and streamline operations.
There are many benefits to implementing a CRM system for service businesses. Some of the most notable benefits include:
Improved Customer Service
- CRM systems provide a centralized location for customer data, making it easy for customer service representatives to access customer information and resolve issues quickly and efficiently.
- CRM systems can also be used to track customer interactions, so that businesses can identify trends and improve their customer service processes.
Increased Sales
- CRM systems can help businesses identify and target potential customers. By tracking customer data, businesses can identify customers who are likely to be interested in their products or services.
- CRM systems can also be used to track sales opportunities, so that businesses can close deals more quickly and efficiently.
Streamlined Operations
- CRM systems can help businesses streamline their operations by automating tasks such as lead generation, marketing, and customer service.
- By automating these tasks, businesses can free up their employees to focus on more important tasks, such as building relationships with customers and growing their business.
Key Features of CRM for Services

Customer relationship management (CRM) systems offer a comprehensive suite of functionalities tailored specifically to meet the unique needs of service organizations. These features empower businesses to effectively manage customer interactions, streamline service delivery, and enhance overall customer satisfaction.
Key features of CRM for services include:
Customer Data Management
CRM systems provide robust customer data management capabilities, enabling businesses to capture, store, and manage all relevant customer information in a centralized repository. This includes customer contact details, purchase history, service interactions, and preferences. By consolidating customer data, businesses gain a comprehensive view of each customer’s journey, allowing them to tailor personalized experiences and deliver exceptional service.
Service Ticketing
Service ticketing is a crucial feature of CRM for services. It allows businesses to efficiently track and manage customer service requests, complaints, and inquiries. Each service ticket contains detailed information about the customer’s issue, the status of the request, and any follow-up actions required.
This streamlined approach ensures that customer requests are handled promptly and effectively, reducing resolution times and improving customer satisfaction.
Knowledge Management
Knowledge management is essential for service organizations to ensure that their teams have access to the information they need to resolve customer issues quickly and efficiently. CRM systems provide a centralized knowledge base where businesses can store and organize relevant articles, FAQs, troubleshooting guides, and other resources.
This enables service representatives to quickly find the information they need to assist customers, reducing resolution times and improving the overall quality of service.
Implementation of CRM in Services

Implementing CRM for service businesses involves several key steps:
Planning Stage
- Define business objectives and goals for CRM implementation.
- Conduct a thorough analysis of existing customer processes and pain points.
- Select a CRM solution that aligns with business needs and industry best practices.
- Develop a comprehensive implementation plan, including timelines, resources, and responsibilities.
Execution Stage
- Install and configure the CRM system according to the implementation plan.
- Migrate data from existing systems into the CRM.
- Train employees on the new CRM system and its functionality.
- Monitor the implementation process and make necessary adjustments.
Evaluation Stage
- Track key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the effectiveness of the CRM implementation.
- Gather feedback from users and customers to identify areas for improvement.
- Make ongoing adjustments to the CRM system to optimize performance and meet changing business needs.
Best Practices for CRM in Services
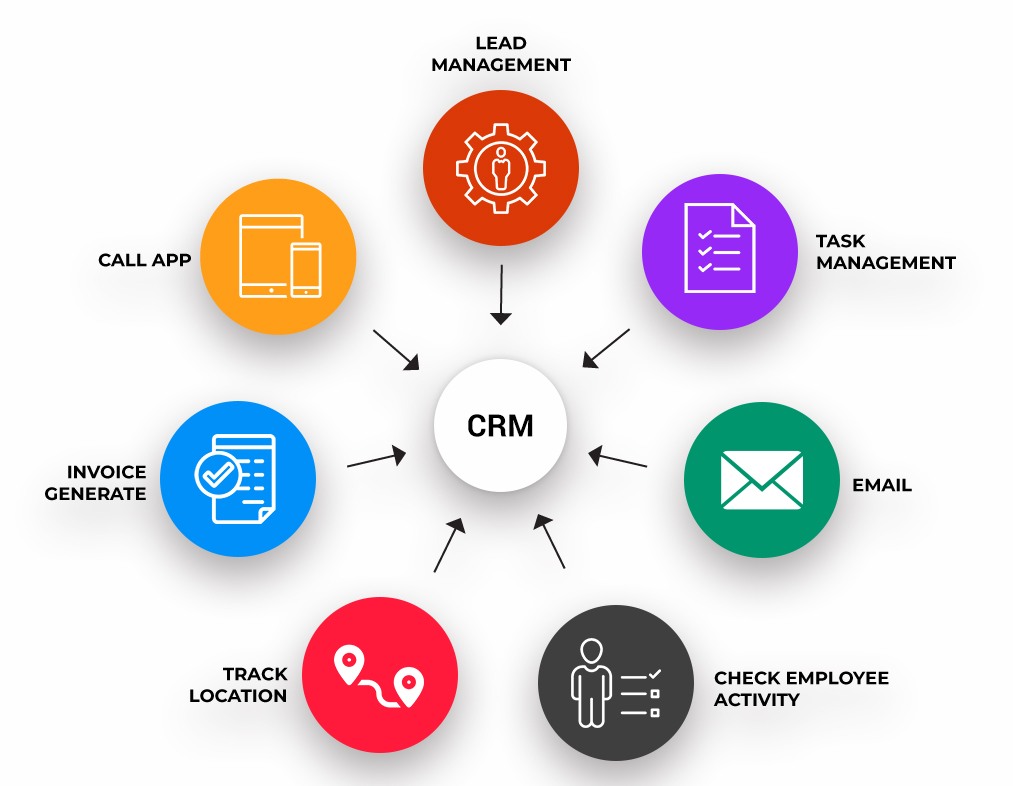
Effective CRM implementation in service organizations requires adherence to best practices that optimize data management, automate processes, and enhance customer engagement. These best practices ensure seamless service delivery, improved customer satisfaction, and increased operational efficiency.
Data Management, Crm in services
- Establish a centralized customer database to consolidate customer information from multiple touchpoints.
- Implement data cleansing and enrichment processes to maintain data accuracy and completeness.
- Leverage data analytics to identify customer trends, preferences, and areas for improvement.
Process Automation
- Automate repetitive tasks such as case management, appointment scheduling, and service order fulfillment.
- Implement workflow automation to streamline processes and reduce manual errors.
- Integrate CRM with other business systems to eliminate data silos and improve operational efficiency.
Customer Engagement
- Personalize customer interactions based on their preferences and history.
- Provide multiple channels for customer support, including phone, email, chat, and social media.
- Monitor customer feedback and use it to improve service quality and customer satisfaction.
Integration with Other Systems
Integrating CRM with other business systems is crucial to streamline operations and enhance data visibility across the organization. It allows for seamless data flow, eliminates data silos, and improves overall efficiency.
By integrating CRM with other systems, businesses can gain a comprehensive view of customer interactions, automate workflows, and improve collaboration among different departments.
Marketing Automation
- Integrate CRM with marketing automation systems to automate marketing campaigns, track customer engagement, and nurture leads.
- This integration enables personalized marketing campaigns, improved lead scoring, and automated lead qualification.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
- Integrate CRM with ERP systems to connect customer data with order processing, inventory management, and financial transactions.
- This integration provides real-time visibility into customer orders, reduces errors, and improves customer service.
Billing Systems
- Integrate CRM with billing systems to automate invoice generation, payment processing, and revenue tracking.
- This integration eliminates manual data entry, improves billing accuracy, and streamlines the revenue collection process.
6. Measurement and Reporting
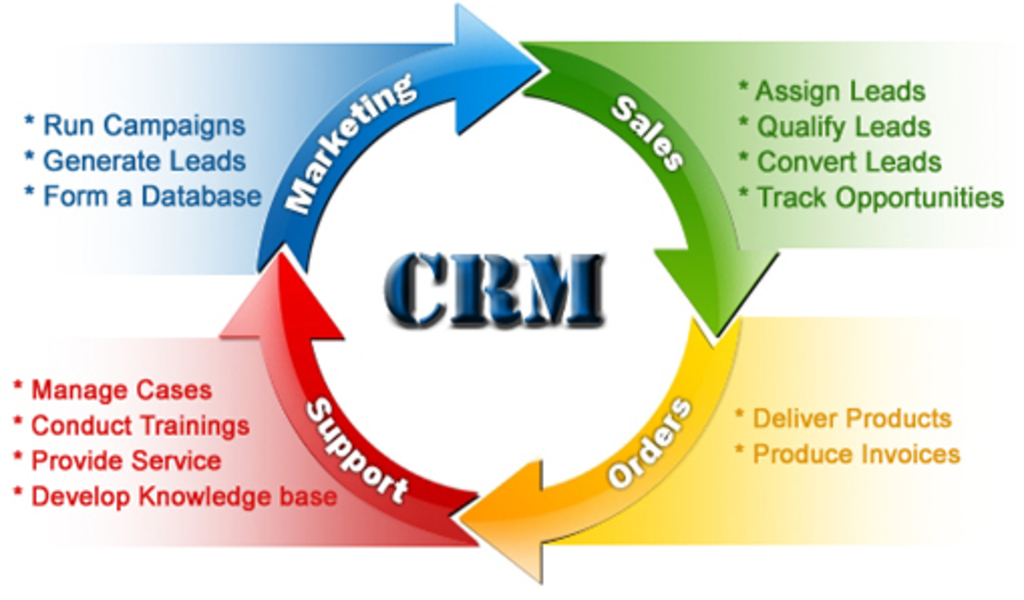
Evaluating the effectiveness of CRM in services is crucial for optimizing performance and driving continuous improvement. Key metrics provide valuable insights into the impact of CRM on customer satisfaction, efficiency, and revenue generation.
To measure the effectiveness of CRM in services, organizations should consider the following key metrics:
Customer Satisfaction
- Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT)
- Net Promoter Score (NPS)
- Customer Effort Score (CES)
These metrics measure the overall satisfaction of customers with the service experience and their likelihood to recommend the organization to others.
Resolution Time
- Average Resolution Time (ART)
- First Response Time (FRT)
These metrics measure the efficiency of the service team in resolving customer issues and inquiries promptly.
Revenue Generated
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV)
- Average Revenue Per Customer (ARPC)
These metrics assess the financial impact of CRM on revenue generation and customer retention.
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) | Measures the overall satisfaction of customers with the service experience |
| Net Promoter Score (NPS) | Measures the likelihood of customers to recommend the organization to others |
| Customer Effort Score (CES) | Measures the ease with which customers can resolve their issues |
| Average Resolution Time (ART) | Measures the average time taken to resolve customer issues |
| First Response Time (FRT) | Measures the time taken to provide an initial response to customer inquiries |
| Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV) | Measures the total revenue generated by a customer over their lifetime |
| Average Revenue Per Customer (ARPC) | Measures the average revenue generated per customer |
Future Trends in CRM for Services
The future of CRM for services organizations is shaped by emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and predictive analytics. These technologies enhance customer experiences, improve operational efficiency, and provide actionable insights for service providers.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- AI-powered chatbots provide 24/7 customer support, resolving queries and automating routine tasks.
- AI algorithms analyze customer data to identify patterns, preferences, and potential issues, enabling personalized service recommendations.
- AI-driven predictive analytics forecast customer behavior, allowing service organizations to proactively address potential problems and deliver proactive support.
Impact of Machine Learning (ML)
- ML algorithms continuously learn from customer interactions, improving the accuracy and efficiency of AI-powered systems.
- ML models identify customer segments based on their behavior, preferences, and service history, enabling targeted marketing campaigns and tailored service offerings.
- ML algorithms automate data analysis, generating insights that help service organizations understand customer trends and improve decision-making.
Impact of Predictive Analytics
- Predictive analytics models analyze historical data and identify patterns to forecast customer behavior and service needs.
- Predictive analytics helps service organizations prioritize customer outreach, predict service demand, and allocate resources efficiently.
- Predictive models can identify customers at risk of churn, enabling service providers to take proactive measures to retain them.
End of Discussion
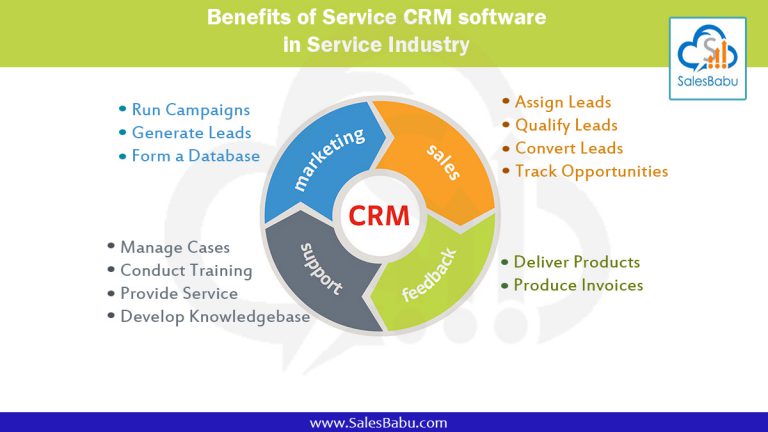
In conclusion, CRM in services has become an indispensable tool for businesses seeking to deliver exceptional customer experiences and achieve operational excellence. By embracing CRM’s transformative power, service organizations can gain a competitive edge, build lasting customer relationships, and drive sustained growth.
FAQ Compilation: Crm In Services
What are the benefits of implementing CRM in services?
CRM in services offers numerous benefits, including improved customer satisfaction, streamlined service processes, increased efficiency, enhanced collaboration, and data-driven decision-making.
How does CRM help service businesses manage customer data?
CRM provides a centralized platform to store and manage all customer data, including contact information, purchase history, service interactions, and preferences. This data can be used to create personalized experiences and deliver tailored services.
What are the key features of CRM for service organizations?
Key features of CRM for service organizations include customer data management, service ticketing, knowledge management, case management, and reporting and analytics.
